Pharmacovigilance Audit and Inspections in China
Internal Audit
Pharmacovigilance audit is a vital process that reviews the drug safety
system to ensure it meets regulations, guidelines, and standard operating
procedures. It involves internal or external auditors who are independent
of the system. Internal auditors, part of the safety or quality assurance
team, conduct periodic reviews, while external auditors provide an
objective assessment.
The audit evaluates various aspects, including the organizational
structure, standard procedures, safety database, signal detection, risk
management, and adverse event reporting. It assesses data quality,
identifies system gaps, and provides recommendations for improvement.
Compliance with regulations and guidelines is a key focus of
pharmacovigilance audits. The audit team ensures adherence to Good
Pharmacovigilance Practice (GVP) and International Council for
Harmonization (ICH) guidelines, ultimately enhancing drug safety. China
GVP also described the audit requirement1:
Chapter II Quality Management
Section 2 Internal Audits
Article 11 Holders shall conduct periodic internal audits (hereinafter
referred to as “internal audits”) to review various systems, procedures,
and their implementation status, and to assess the suitability, adequacy,
and effectiveness of the pharmacovigilance system. When any significant
changes occur to the pharmacovigilance system, internal audits should be
carried out in a timely manner. The internal audit can be carried out
independently, systematically, and comprehensively by the holder’s
designated personnel, or by external personnel or experts.
Article 12 An audit plan shall be developed before the internal audit. The
plan should include internal audit objectives, scope, methods, standards,
auditors, audit records and reporting requirements, etc… While
developing the plan, key pharmacovigilance activities, key positions, and
previous audit results, etc. should be considered.
Article 13 Records shall be kept for internal audits, including the basic
information, content and results of the audit, and a written report shall
be formed.
Article 14 For the findings identified in the internal audit, holders
shall investigate the root cause and take corresponding corrective and
preventive actions. The corrective and preventive actions should be
followed-up and assessed.
Reference: 1. China Good Pharmacovigilance Practice
Announcement of the NMPA on the Publication of China Good
Pharmacovigilance Practice (No. 65 of 2021)
Should you have any queries or seeking for consultation, please contact
us via online chat or email.
Regulatory Inspections
The overarching authority responsible for drug and pharmacovigilance
inspections is China’s National Medical Products Administrations (NMPA).
The pharmacovigilance audit and inspection work are conducted in groups
formed by the Drug Inspection Institutions. The complete inspection is
fulfilled with the support of the following four institutions:
- Drug Testing Institutions
- Centre for Drug Evaluation (CDE)
- Centre for Drug Reevaluation (CDR)
- National Centre for ADR Monitoring.
In addition, the legal departments will be involved upon legal issues.
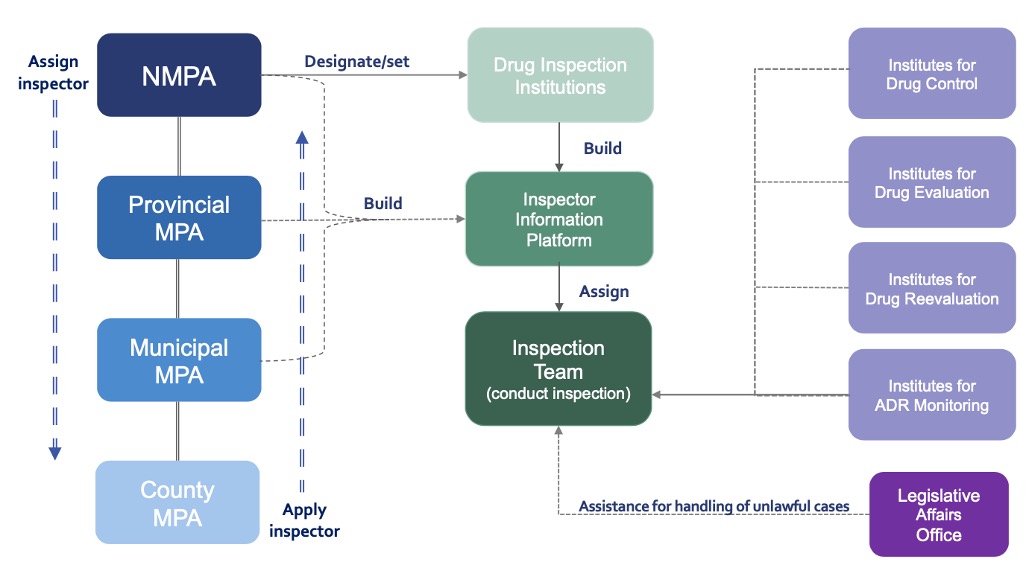
Authority for Supervision of Drugs
- NMPA and Local MPA including Provincial, Municipal, and County level are
responsible to set up and designate pharmaceutical and pharmacovigilance
inspection institutions in accordance with law.
- NMPA shall be responsible for forming annual supervision and inspection
plan, arranging inspection tasks, or organizing inspections, and work
according to the Report on Comprehensive Evaluation of Drug Inspection
and relevant evidence materials.
- NMPA shall set up a professional team of specialized drug inspectors,
implement multi-level & classification system for inspectors, formulate
the standards of duties and duties of inspectors at different levels as
well as requirements for comprehensive capability, and establish strict
criteria for relevant positions.
- NMPA and the drug inspection institution is responsible for establishing
inspector database and inspector information platform to realize the
information sharing and coordination of inspectors at all levels from
national to county-level.
Institutions for Drug Inspection
- Drug inspection institutions carry out inspections according to China’s
laws and regulations on drug supervision before issuing the
Comprehensive Evaluation Report on Drug Inspection and be responsible
for daily management of professional inspector team and implementation
of inspection plans and tasks.
- Other departments such as drug inspection, review, evaluation, and
adverse drug reaction (ADR) monitoring established shall provide
technical support during the inspection.
- Drug inspection institutions shall establish a quality management system
to continuously improve the quality of drug inspection work.
- The drug supervision authority or drug inspection institution is
responsible for establishing inspector database and inspector
information platform to promote the information sharing and coordination
of inspection within national, provincial, and county levels.
Drug Inspection Group
- The inspection group should be set up by the pharmacovigilance
inspection team to carry out the audit.
- Usually, an inspection group consists of more than 2 qualified
inspectors
- The team leader is responsible for the inspection team. When necessary,
experts in relevant fields can be selected to participate in the
inspection
Authority Inspection Key Points
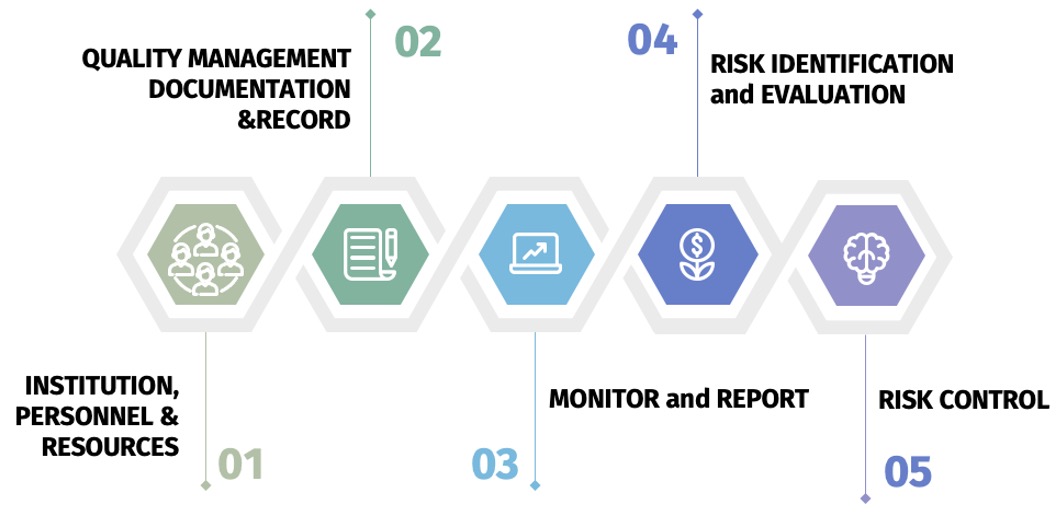
According to Guidelines for Pharmacovigilance Inspections1 released by the
NMPA, a total of 100 checking items are listed. 12 of which are critical
and 40 are major points.
This is the 5 key points for authority inspection.
- Institution, personnel and resources, refers to 22 articles from GVP
- Quality management, documentation and record, refers to 28 articles
- Monitor and report, refers to 17 articles.
- Risk identification and evaluation, refers to 19 articles.
- Risk control, refers to 14 articles.
Throughout the first year of 2022, the authorities overseeing drug
testing, review, evaluation, and adverse drug reaction (ADR) monitoring
focused their attention primarily on the first two points. These areas
were given priority due to their direct accessibility and evaluative
nature. In addition, the authorities made efforts to understand the
operational practices within pharmaceutical companies. As we enter 2023,
inspection groups have gained valuable experience, which will be reflected
in their increased emphasis on activities such as signal detection,
reporting, and risk control, among others.
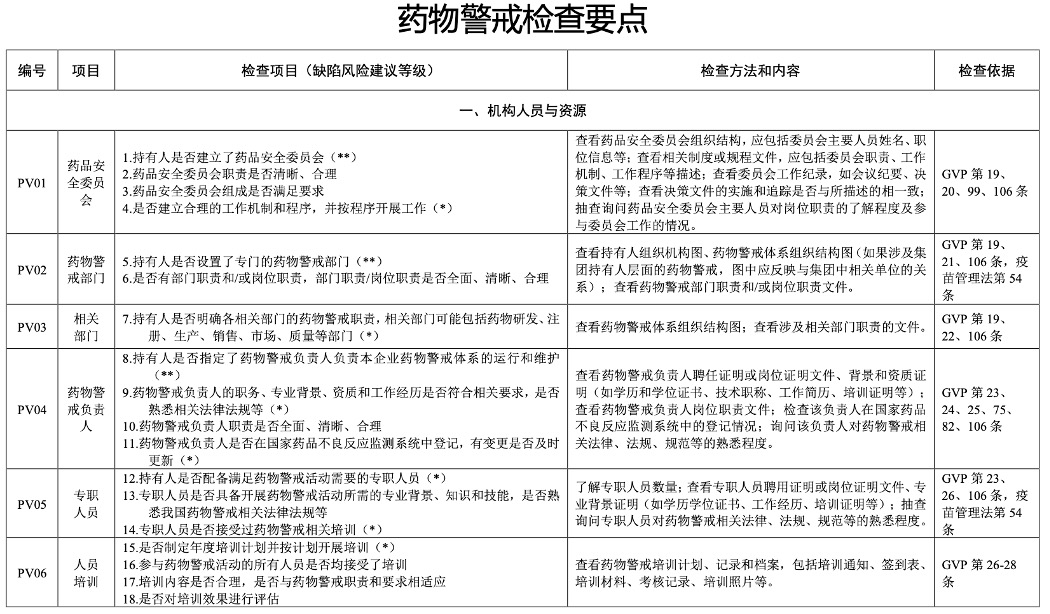
The following is part of Pharmacovigilance Inspection Check Points in the
official Guidelines for Pharmacovigilance Inspections.
For full PDF (original Chinese and English translated version) of
Guidelines for Pharmacovigilance Inspections and the Annex –
Pharmacovigilance Inspection Check Points Table, please contact us via
online chat or email.
Reference:
1. Guidelines for Pharmacovigilance Inspections,
Announcement by the NMPA on the issuance of the Guidelines for
Pharmacovigilance Inspections No. [2022] 17


